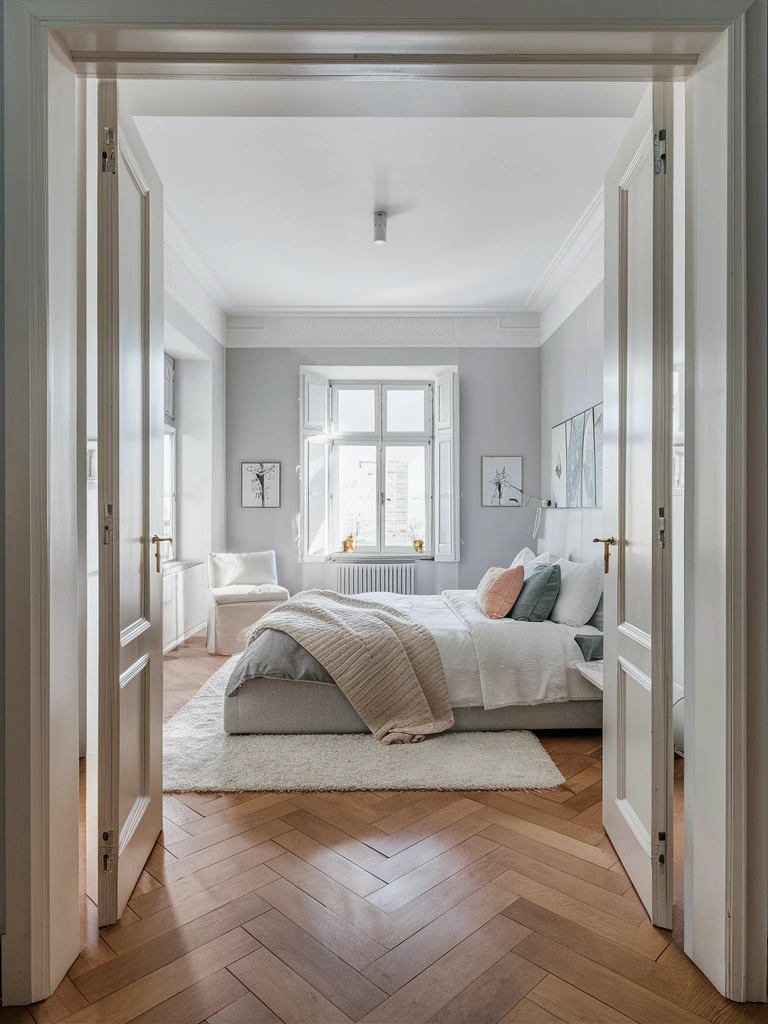
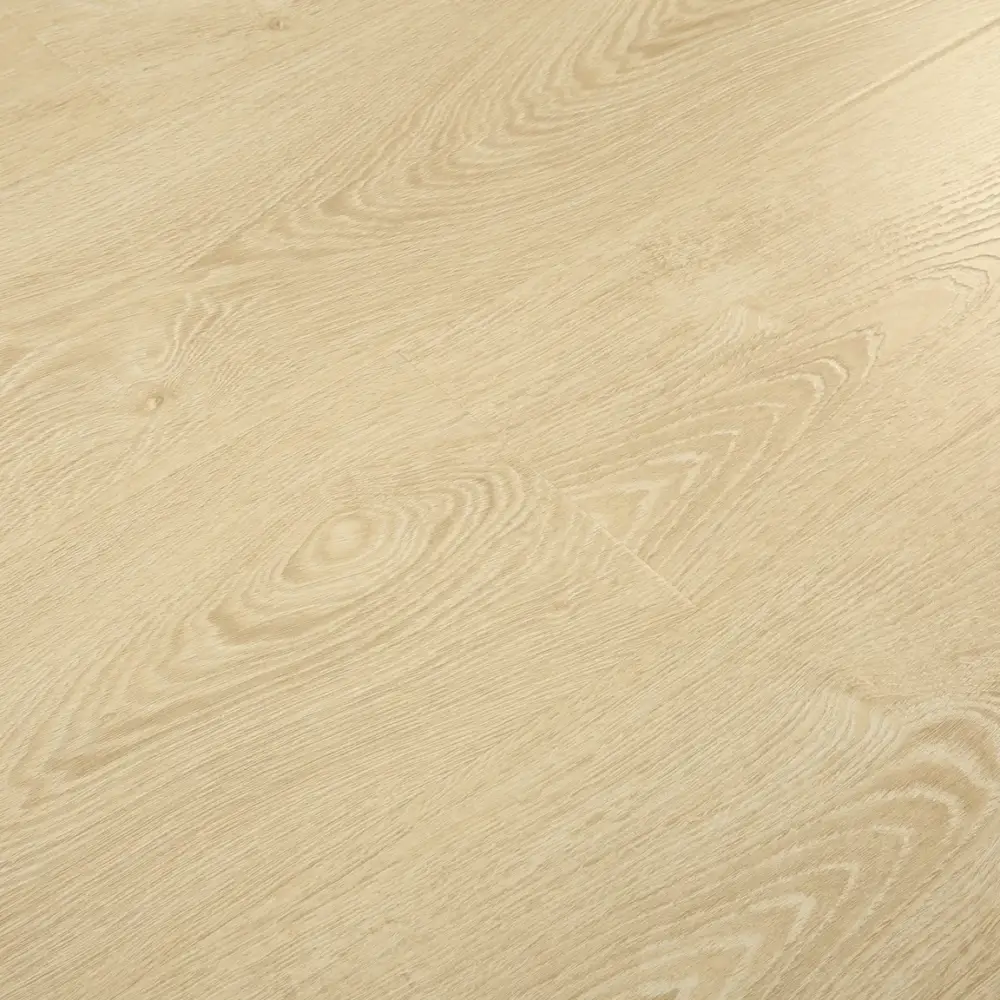
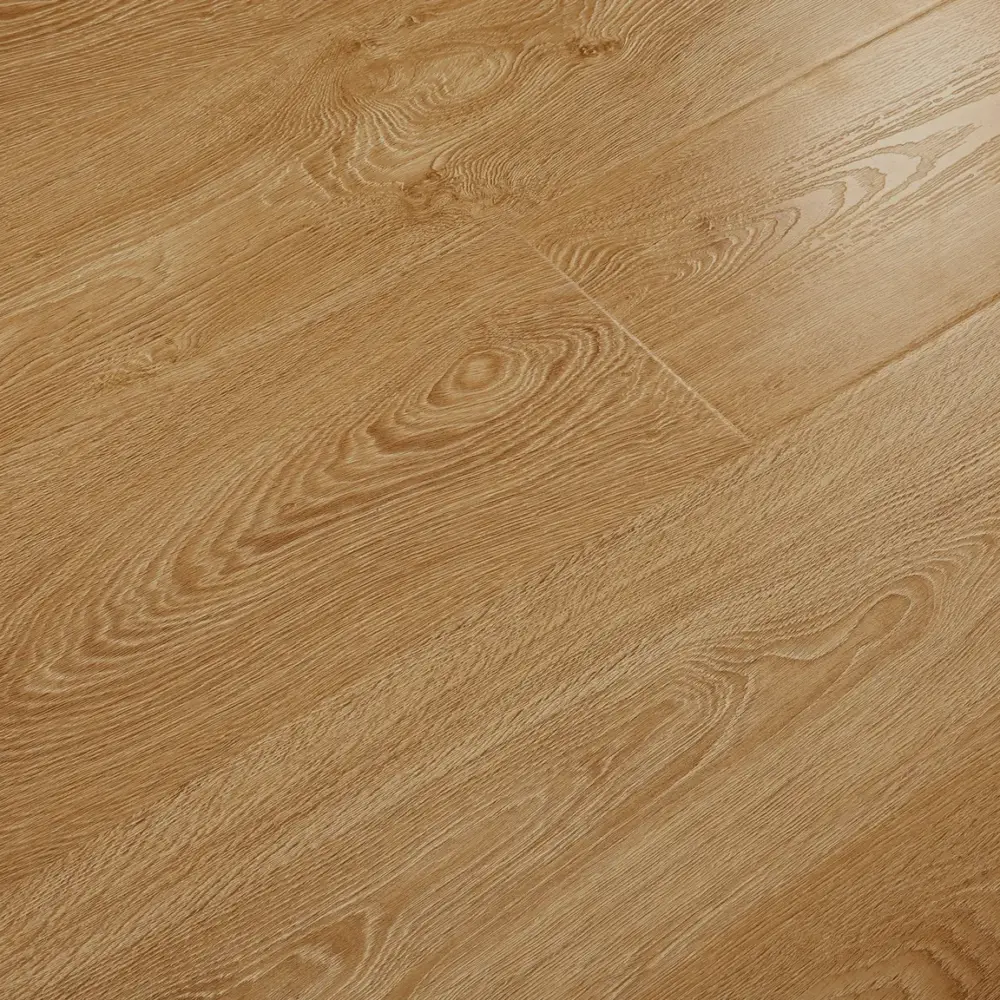
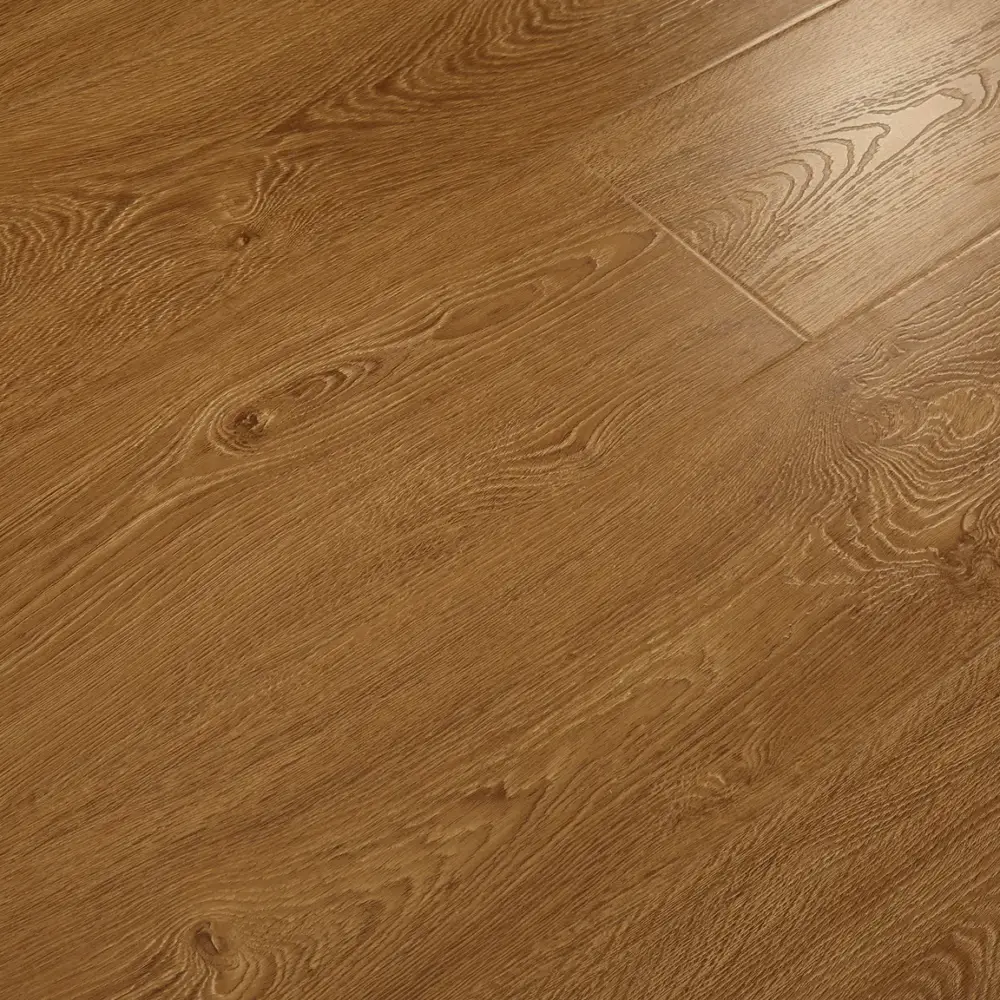
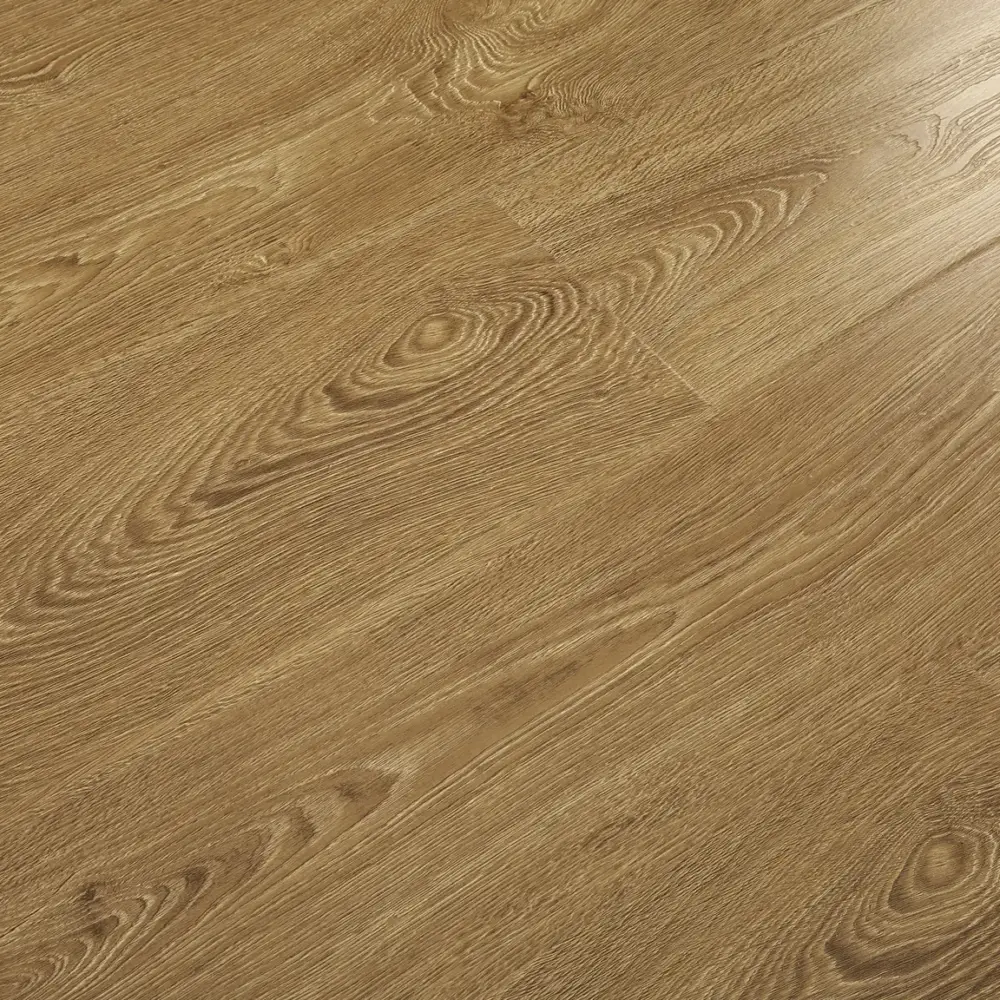
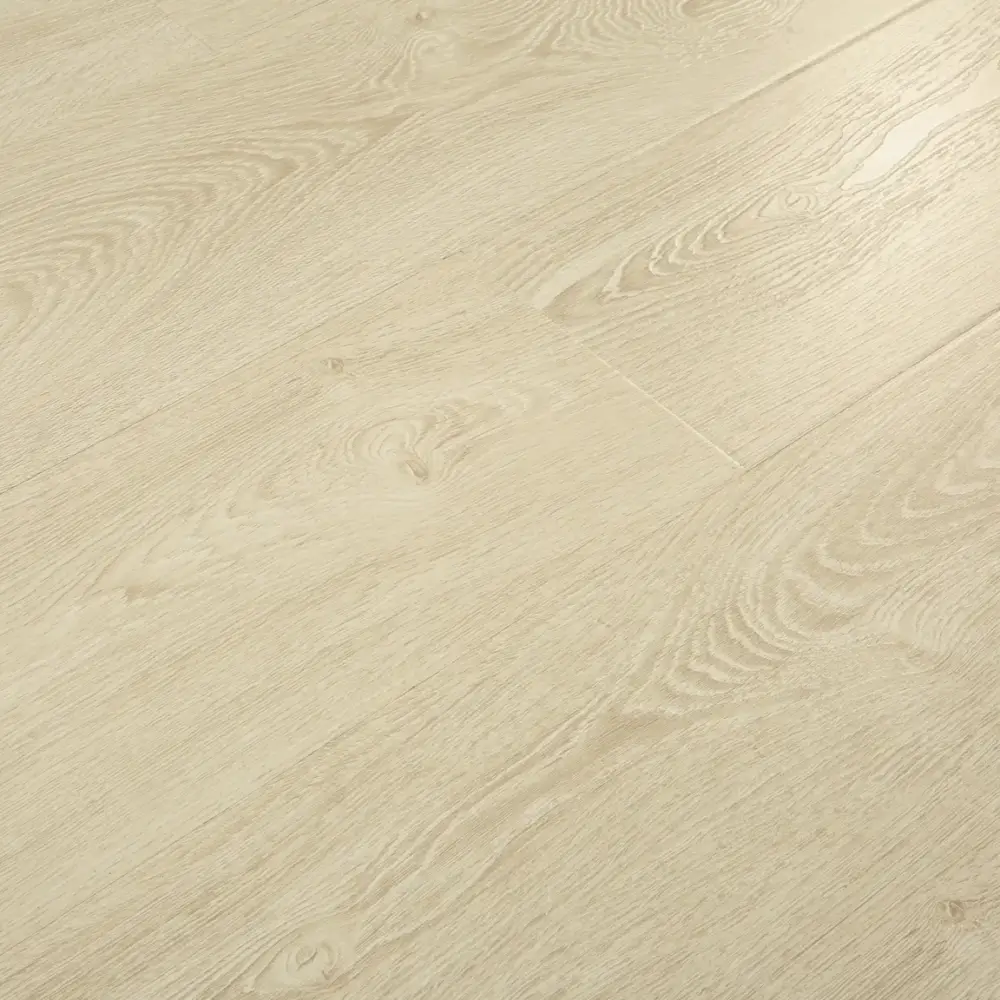
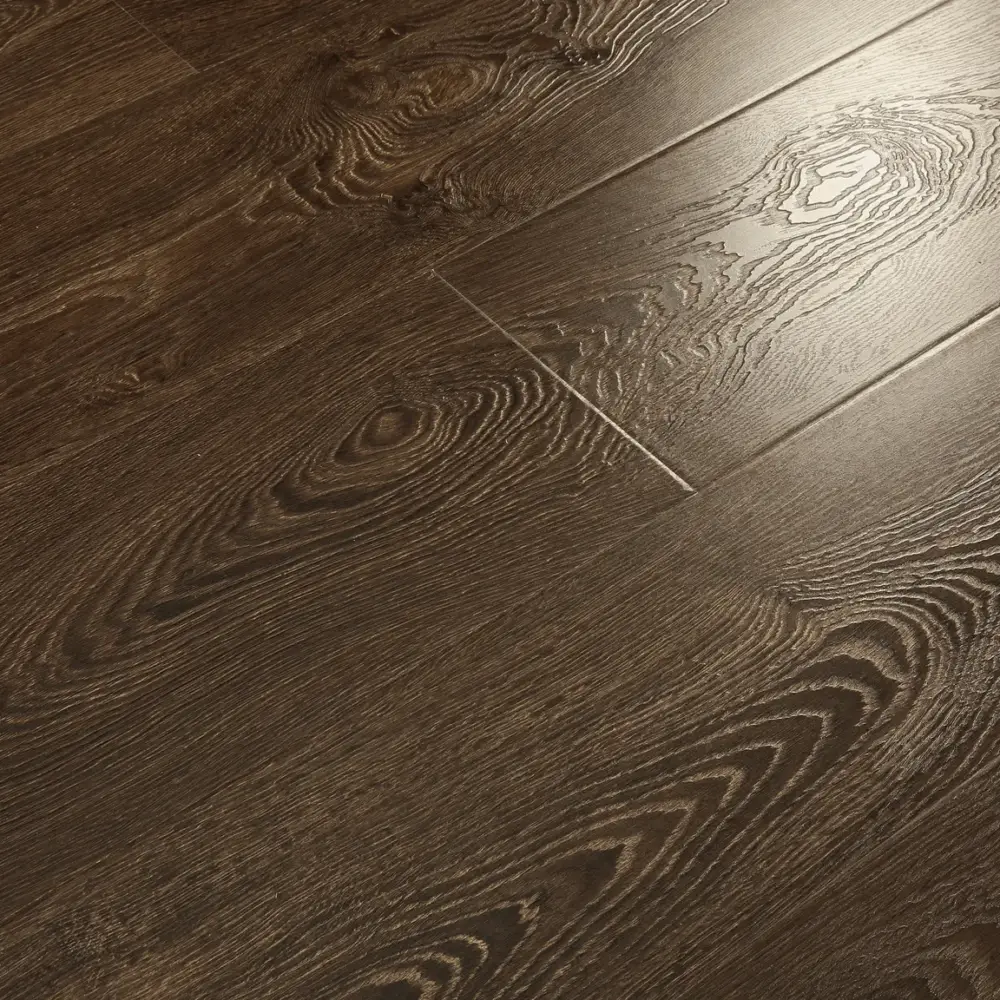
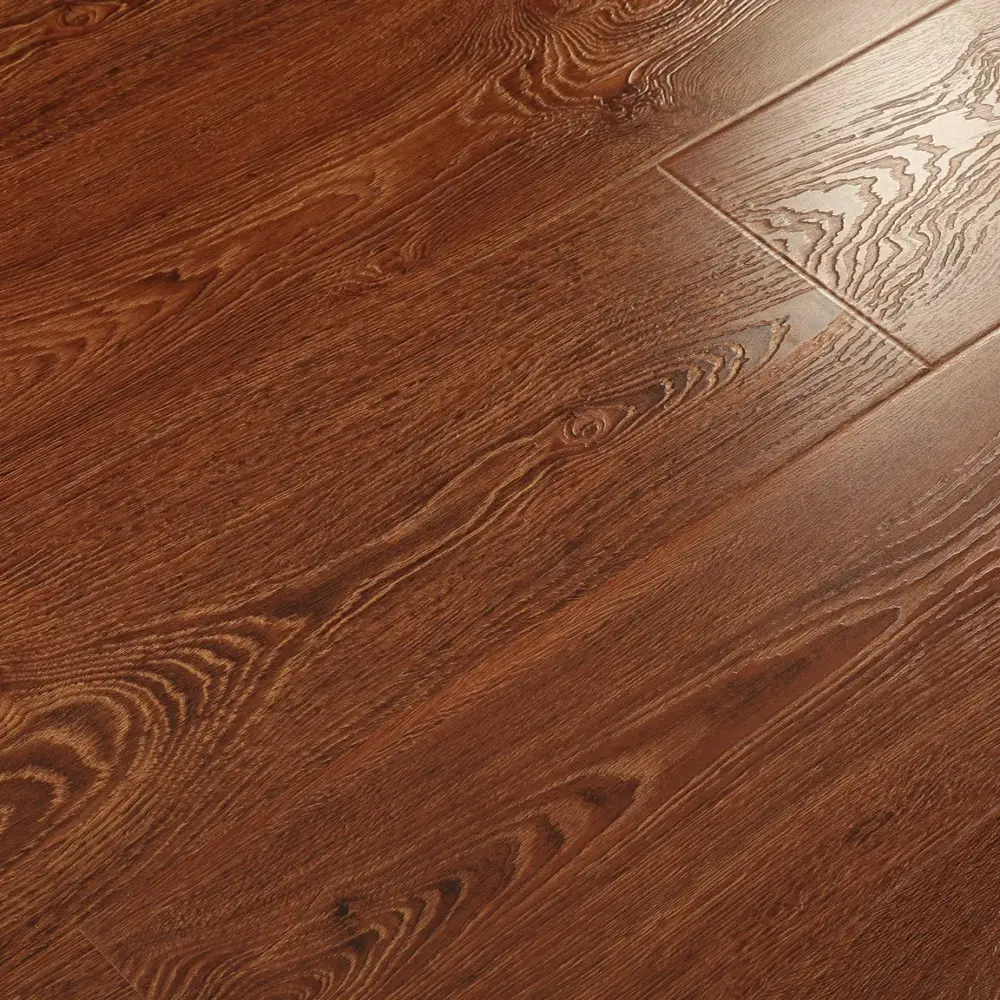
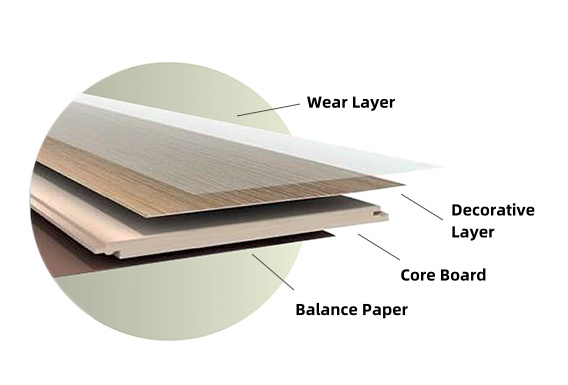
Laminate flooring is a multi-layer synthetic flooring product that mimics the look of hardwood, stone, or tile. It consists of four main layers: a wear layer, a decorative layer, a core layer, and a backing layer. The wear layer provides protection against scratches, stains, and fading, while the decorative layer features a printed design that replicates the desired material’s appearance.
Structure and Composition
The core layer, typically made of high-density fiberboard (HDF) or particleboard, provides stability and moisture resistance. The backing layer, often made of melamine resin, acts as a moisture barrier and helps the planks lay flat. These layers are fused together using heat and pressure, creating a durable and long-lasting flooring solution.

Advantages of Laminate Flooring
Laminate flooring offers several advantages over traditional flooring options:
- Affordability: It is generally less expensive than hardwood or stone flooring.
- Easy installation: Laminate planks can be installed as a floating floor, making it a DIY-friendly option.
- Low maintenance: The wear layer protects against scratches, stains, and fading, requiring minimal maintenance.
- Variety of designs: Laminate flooring is available in a wide range of styles, mimicking various wood species and stone patterns.
- Durability: With proper care, laminate flooring can last for many years.
User Cases and Applications
Laminate flooring is suitable for various residential and commercial applications, including:
- Living rooms, bedrooms, and hallways in homes
- Offices, retail spaces, and other commercial settings
- Basements and other moisture-prone areas (with proper underlayment)
- Rental properties or temporary living spaces
Its versatility, affordability, and ease of installation make laminate flooring a popular choice for homeowners, landlords, and businesses alike.











